processing tips
Part 11: A Processor's Most Important Job
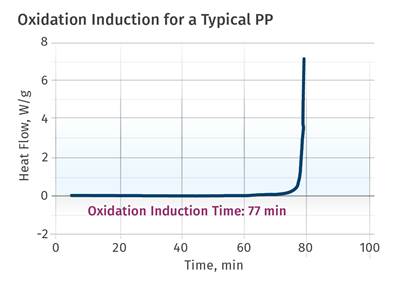
It’s the processors job to ensure molded parts contain enough stabilizer to perform to the expectations of the end use.
Read MoreA Gel By Any Other Name...
Gels…unmelt…contaminants…inclusions…whatever you call them, you want to avoid them. Proper maintenance and good housekeeping—lids on boxes, closed hopper doors, core-free reclaim systems—go a long way towards defect-free product.
Read MoreExtrusion: Head Pressure and Output Stability
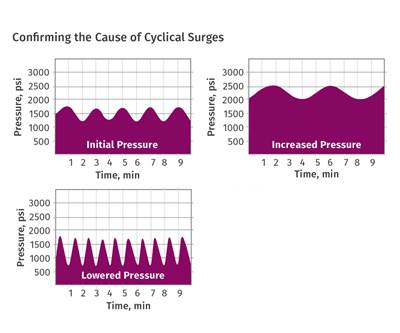
Use drag- and pressure-flow equations to analyze fluctuating output.
Read MoreInjection Molding: Sliding vs. Locking Ring—Which Non-Return Valve Is Right for You?
The locking-ring style appears to dominate the market, as most believe it makes a make a better seal and leaks less. But is this really so?
Read MoreA Processor's Most Important Job, Part 9: Avoid Molded-In Stress
How to establish molding conditions that minimize internal stress in a part.
Read MoreUp to Snuff on Scientific Molding? Then it’s Time to Mold ‘Systematically’
Scientific molding is centered around learning about key molding principles and theories. The strategic application of those principles and theories is what’s known as systematic molding.
Read MoreHow to Improve Production of Catheters and Stents
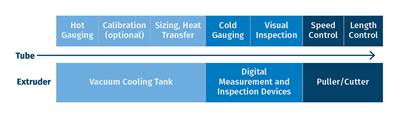
Advances in downstream extrusion equipment have boosted production control.
Read MoreReducing Low-Level Background Gels in PE Film
While considered acceptable in many cases, they need not be tolerated and are usually attributable to minor screw-design flaws. Here’s some advice on what to do about them.
Read MorePellet to Gate Control: The Value of a Holistic View of Melt Management
Molders tend to think about the elements of a melt-delivery system, from screw to hot-runner gate, in isolation from each other. But taking an integrated view of the whole system can have big consequences for cycle time, part quality, scrap rates, and energy consumption.
Read MoreInjection Molding: Is There a ‘Most-Important’ Process Parameter?
A case can be made for multiple variables—fill balance, fill time, injection pressure, cavity pressure—as most important. But there is something else altogether that is essential to successful injection molding.
Read More